Nest.js 개요
Nest.js
- a framework for building efficient, scalable Node.js server-side applications
- typescript 사용
- OOP, FP, FRP 모두 결합
- default는 싱글톤 패턴을 사용
- 싱글톤 패턴 : 각 클래스가 하나의 인스턴스만 생성하고, 어떤 프로바이더든지 같은 인스턴스를 공유해 사용하는 패턴
- init : https://github.com/nestjs/typescript-starter
IoC(Inversion of Control) Container
- IoC를 구현하는 프레임워크로, 객체를 관리하고 생성을 책임지고 의존성을 관리하는 컨테이너이다.
- 일반적인 라이브러리 호출과는 다르게, 외부 라이브러리 코드에서 프로그래머가 작성한 코드를 호출하는 형식 (IoC)
Request Lifecycle
- incoming request
- globally bound middleware
- module bound middleware
- global guards
- controller guards
- route guards
- global interceptors (pre-controller)
- controller interceptors (pre-controller)
- route interceptors (pre-controller)
- global pipes
- controller pipes
- route pipes
- route parameter pipes
- controller (method handler)
- service (if exist)
- route interceptors (post-request)
- controller interceptors (post-request)
- global interceptor (post-request) 19 exception filters (route, then controller, then global)
- server response
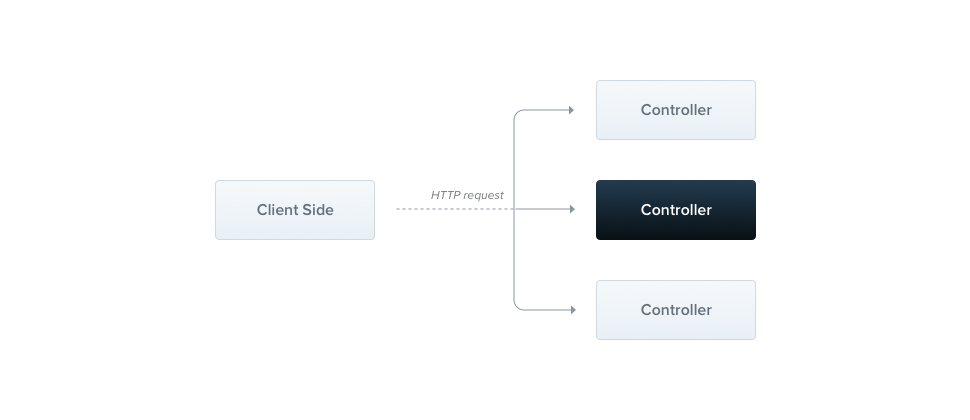
Controllers
import { Controller, Get } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('cats')
export class CatsController
@Post()
create(): string {
return 'This action adds a new cat';
}
@Get()
findAll(): string {
return 'This action returns all cats';
}
}
- routing mechanism (특정 URI에 대한 요청이 여기에 걸림)
- DTO (Data Transfer Object) 사용
Providers
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Cat } from './interfaces/cat.interface';
@Injectable() /** Nest IOC container에 의해 manage된다는 것을 선언 **/
export class CatsService {
private readonly cats: Cat[] = [];
create(cat: Cat) {
this.cats.push(cat);
}
findAll(): Cat[] {
return this.cats;
}
}
- Nest.js의 대부분의 클래스 (services, repositories, …) 등이 provider로써 취급된다.
- class constructor의 매개변수에 private로 넘겨줌으로써 선언과 초기화를 동시에 할 수 있다.
- SOLID하게 구현하는 게 좋다.
SOLID (객체지향 개발 5대 원리)
- SRP (단일책임의 원칙: Single Responsibility Principle)
“하나의 클래스를 수정해야되는 이유는 오직 한 가지여야 한다.”
- OCP (개방폐쇄의 원칙: Open Close Principle)
“소프트웨어 개체(클래스, 모듈, 함수 등)는 확장에 대해서는 열려있어야 하고, 수정에 대해서는 닫혀있어야 한다.”
- LSP (리스코브 치환의 원칙: The Liskov Substitution Principle)
“서브 타입은 언제나 자신의 기반 타입(base type) 으로 교체할 수 있어야 한다.”
- ISP (인터페이스 분리의 원칙: Interface Segregation Principle)
“클라이언트가 사용하지 않는 메소드에 영향받지 않아야 한다.”
- DIP (의존성역전의 원칙: Dependency Inversion Principle)
“클래스를 참조할 일이 있을 때 그 클래스를 직접 참조하지 말고 그 대상의 추상 클래스를 만들어서 참조해야 한다”
Guards
import { Injectable, CanActivate, ExecutionContext } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable()
export class AuthGuard implements CanActivate {
canActivate(
context: ExecutionContext,
): boolean | Promise<boolean> | Observable<boolean> {
const request = context.switchToHttp().getRequest();
return validateRequest(request);
}
}
- 해당 요청에 적법한 사용자인지를 검사하는 로직이 들어간다. (authentication)
- true 반환 : request 진행
- false 반환 : request 거절 (forbiddenException)
Modules
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { CatsController } from './cats.controller';
import { CatsService } from './cats.service';
@Module({ /** decorator provides metadata that Nest makes use of to organize the application structure. **/
imports: [...],
controllers: [CatsController],
providers: [CatsService],
exports: [CatsService]
})
export class CatsModule {}
- imports : 해당 모듈에 임포트된 모듈의 리스트
- controllers : 해당 모듈 내에 정의돼있는, 인스턴스화 해야하는 컨트롤러의 리스트
- providers: 해당 모듈 내에 nest injector 에 의해 인스턴스화 해야하는 프로바이더의 리스트
- exports: 해당 모듈을 임모트할 다른 모듈에서 사용되어야 하는 프로바이더의 리스트
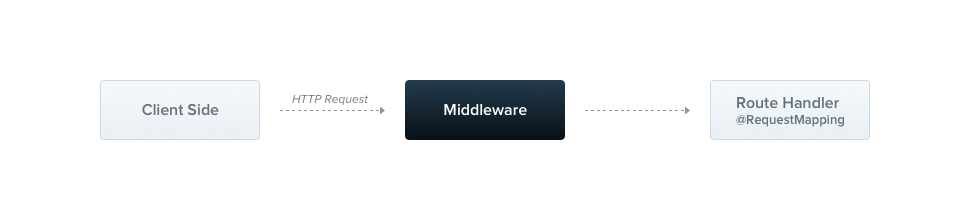
Middleware
import { Injectable, NestMiddleware } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request, Response, NextFunction } from 'express';
@Injectable()
export class LoggerMiddleware implements NestMiddleware {
use(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
console.log('Request...');
next();
}
}
- req, res 객체를 조작할 수 있다.
Interceptors
import { Injectable, NestInterceptor, ExecutionContext, CallHandler } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { tap } from 'rxjs/operators';
@Injectable()
export class LoggingInterceptor implements NestInterceptor {
intercept(context: ExecutionContext, next: CallHandler): Observable<any> {
console.log('Before...');
const now = Date.now();
return next
.handle() /** If you don't call handle(), the route handler method won't be executed at all. **/
.pipe(
tap(() => console.log(`After... ${Date.now() - now}ms`)),
);
}
}
- method 실행 전/후 extra 로직을 바인드시킨다.
- 전 : return 이전
- 후 : return 문
Pipes
@Get(':id')
async findOne(@Param('id', ParseIntPipe) id: number) {
return this.catsService.findOne(id);
}
- transformation : string -> number 등의 형변환이 필요한 경우 파이프에서 진행
- validation : 변수 등에 대한 유효성 검증도 할 수 있다.